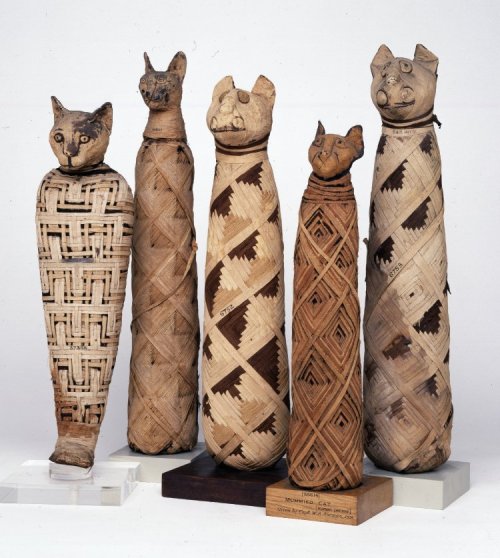

Cat mummies. Source: British Museum.
A recent article about how only about 1/3 of animal mummies in ancient Egypt actually contained the mummified animal in question (with the remaining mummies divided evenly between “bundle of cloth wrapped around mud and sticks” and “bundle with animal parts such as feathers or fur, but no complete skeleton”) made an apparently offhand comment that caught my eye.
While explaining the program — in which researchers from the Manchester Museum and the University of Manchester have CT scanned more than 800 animal mummies — Dr Campbell Price, curator of Egypt and Sudan at Manchester Museum, said:
“Animal mummies were votive gifts. Today you’d have a candle in a cathedral; in Egyptian times you would have an animal mummy. You would go to a special site, [and] buy an animal mummy, using a system of barter. You’d then give it to a priest, who would collect a group of animal mummies and bury them.
…The scale of animal mummification between about 800 BC and into the Roman period was huge. In terms of how many animals were reared and killed, it would have been on an industrial scale. The animals were young and killed when they were quite small. To achieve those numbers you had to have a very specific breeding programme.”
X-ray of kitten mummy inside votive cat figure. Image source: Richard Barnes, National Geographic.
This had honestly never occurred to me, and I was alarmed to discover it was not just a throwaway comment; it was quite true. Though Egyptians had long applied the practice of mummifying pet animals, including dogs (warning: photo of mummified dog face) and cats, as well as sacred animals, such the Apis bulls, sometime during the Late Period in Egyptian history (around 715 BC to 322 BC), the practice of offering mummified, “votive” animals to the god one most wished to intervene in one’s affairs became increasingly popular. In order to satisfy the demand for animal mummies, of which researchers estimate there were more than 70 million, ancient Egyptians actually eventually turned to factory-farming “votive animals” deliberately bred for mummification. The ancient Egyptians may have raised puppies and kittens specifically for slaughter, in special areas next to the temples.
I completely missed that when my middle school social studies class covered ancient Egypt. Interesting that in more than three thousand years we still have not resolved the dichotomy between “pet” animals, whom we love, and “farmed” animals, whom we use….
(Incidentally, we’ve known about the existence of fake, or empty, animal mummies for decades; this recent mass CT scanning has just brought the scale of it to light. It is still not known whether the fake mummies were deliberate scams, a practical effort to deal with the increasing scarcity of some of the rarer species, or simply evidence of differing approaches wherein the entire animal was not always required to make an offering.)
